 +86-15267462807
+86-15267462807
Function: MBBR media provide a surface for the growth of biofilms, which are communities of microorganisms that degrade organic matter.
Types: K1, K3, K5 media, plastic carriers, and other porous materials.
Advantages: High efficiency, low energy consumption, and flexibility.
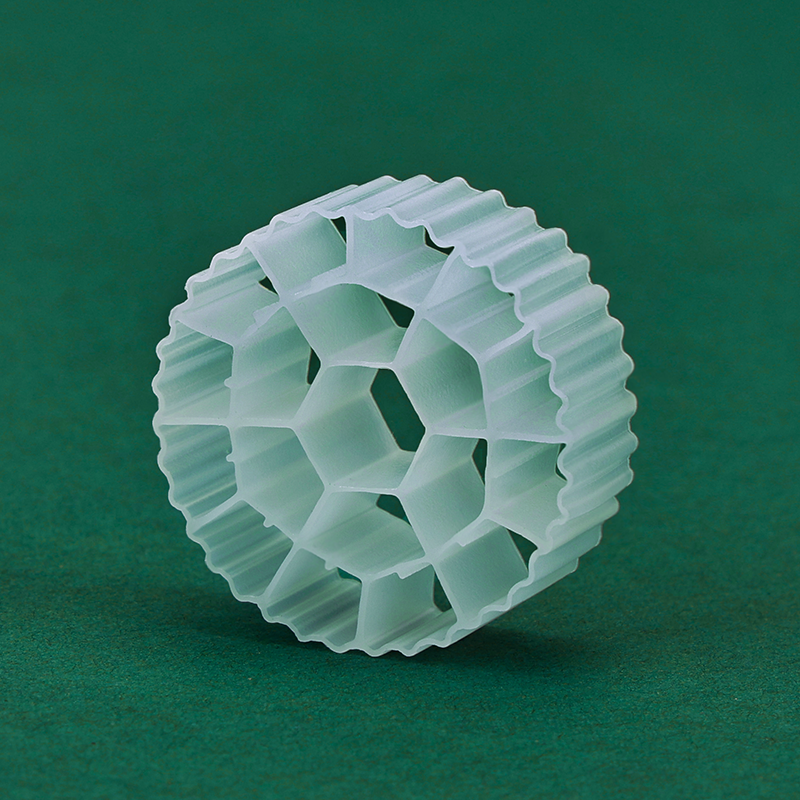

Function: Diffuser media are used in aeration systems to distribute air into water for biological processes.
Types: Fine-pore, coarse-pore, and membrane diffusers.
Advantages: Efficient oxygen transfer, durability, and low maintenance.
Function: Trickling filter media provide a surface for biofilm growth in trickling filter systems.
Types: Rock, plastic, and ceramic media.
Advantages: Simple design, low energy consumption, and effective organic matter removal.
Function: Tube settler media accelerate the settling of particles in sedimentation basins.
Types: Parallel plates, inclined plates, and tube settlers.
Advantages: Increased sedimentation efficiency, reduced basin size, and lower energy consumption.
Function: Sand filtration media remove particles from water through physical filtration.
Types: Silica sand, anthracite, and garnet.
Advantages: Effective particle removal, low cost, and easy maintenance.
Function: Anthracite is a denser form of carbon used in filtration to remove smaller particles and organic matter.
Advantages: Higher filtration efficiency, longer filter run times, and better backwash performance.
Function: DE is a fine, porous material used in DE filters to remove very small particles and turbidity.
Advantages: Extremely high filtration efficiency, excellent turbidity removal, and compatibility with various water sources.
Function: Ion exchange resins are used to remove specific ions from water, such as hardness minerals (calcium and magnesium).
Types: Cation exchange resins, anion exchange resins, and mixed bed resins.
Advantages: Highly selective ion removal, high capacity, and regenerability.
Function: Activated carbon is a porous material used to adsorb organic contaminants, such as taste and odor compounds, from water.
Types: Powdered activated carbon (PAC) and granular activated carbon (GAC).
Advantages: Effective contaminant removal, versatility, and regeneration capability.
Function: Membrane filters are used to remove particles, bacteria, and viruses from water through physical filtration.
Types: Microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis membranes.
Advantages: High removal efficiency, low energy consumption, and versatility.
Function: Ozonation media are used to produce ozone gas, a powerful disinfectant and oxidant.
Types: Corona discharge, dielectric barrier discharge, and ultraviolet (UV) irradiation.
Advantages: Effective disinfection, oxidation of organic contaminants, and minimal byproduct formation.
Function: Chlorination media are used to add chlorine to water for disinfection and oxidation.
Types: Chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, and calcium hypochlorite.
Advantages: Effective disinfection, affordability, and long-term residual disinfection.