 +86-15267462807
+86-15267462807
Tube Settler, also known as tubular settler, is a widely used device in water treatment, especially in the sedimentation stage to improve efficiency and water quality. It is mainly used to accelerate the sedimentation of particles, thereby improving the performance of the entire treatment system. This article will introduce the structural design, working principle and optimization strategy of Tube Settler in detail.
Structural design of Tube Settler
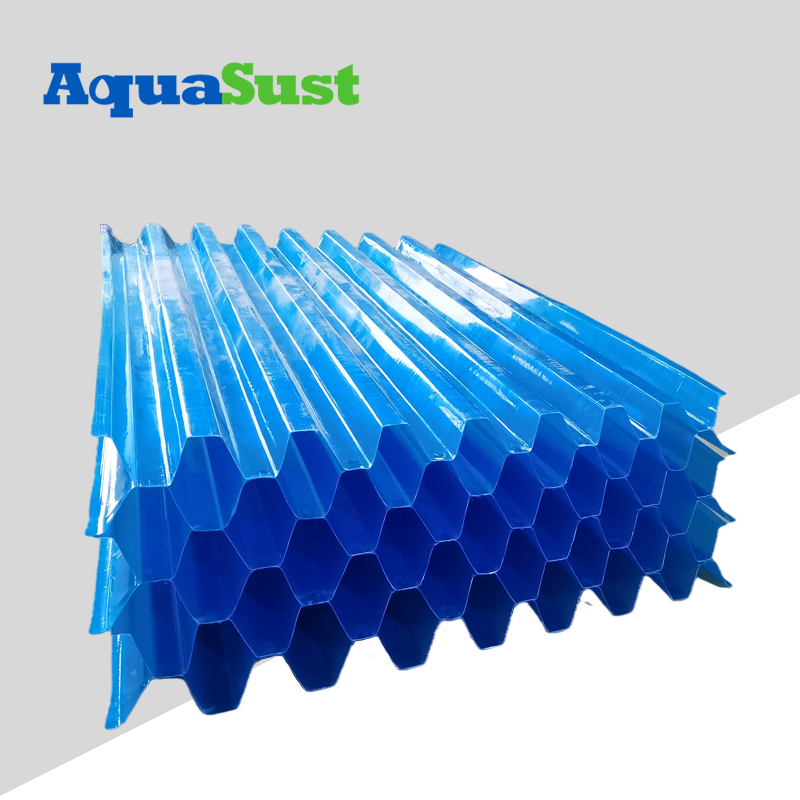
Tube Settler consists of multiple inclined pipes or plate channels, which are usually made of corrosion-resistant materials such as PVC or PP (polypropylene). The design and arrangement of these pipes are carefully designed to maximize the sedimentation efficiency.
Component composition
Settling tube: usually hexagonal, square or circular cross-section, with a length ranging from 600 mm to 1200 mm.
Support structure: ensure that the settling tube maintains the appropriate inclination angle and stability.
Collection system: located at the bottom of the Tube Settler, used to collect the settled sludge and guide the outlet.
Tilt angle
The inclination angle of the settling tube is usually set between 45 degrees and 60 degrees, which is to optimize the sliding path of the particles and increase the sedimentation rate.
Working Principle
1. Water Flow Direction
The treated water contains suspended particles and is first directed to the top of the Tube Settler. As the water enters the inclined settling tubes, its speed and direction are adjusted to accommodate the settling process.
2. Particle Settling
Due to gravity, the heavier suspended particles begin to move downward along the inclined surface of the settling tubes. The tubes are designed to be inclined so that the particles settle before reaching the bottom of the tubes, effectively reducing the vertical distance the particles fall in the water column, thereby accelerating the settling process.
3. Stratified Outflow
The settled water is removed and flows out of the top of the Tube Settler, and most of the suspended particles have been significantly removed. This stratified outflow helps improve the cleanliness and quality of the effluent.
4. Sludge Treatment
The particles that settle to the bottom of the Tube Settler form sludge, which is then concentrated in the sludge collection system at the bottom of the sedimentation tank and treated by periodic or continuous discharge.
Key factors for optimizing settling performance
1. Adjusting the pipe angle
By adjusting the inclination angle of the pipe, the best particle settling path can be found to adapt to different water flow characteristics and particle sizes.
2. Pipe size and shape
Choosing the appropriate pipe size and shape can improve settling efficiency while preventing blockage and water flow disturbance between pipes.
3. Water flow control
Controlling the speed and amount of water flow entering the Tube Settler is key. Too fast water flow will cause particles to fail to settle effectively, while too slow water flow may affect treatment efficiency.
Conclusion
The Tube Settler is an efficient water treatment equipment that can significantly improve the sedimentation efficiency and water quality of water treatment plants through precise structural design and optimized operation strategies. Proper installation and maintenance of the Tube Settler is essential to achieve the best water treatment results. Through these technologies, water treatment facilities can more efficiently treat large volumes of water while ensuring that water quality meets safety and environmental standards.